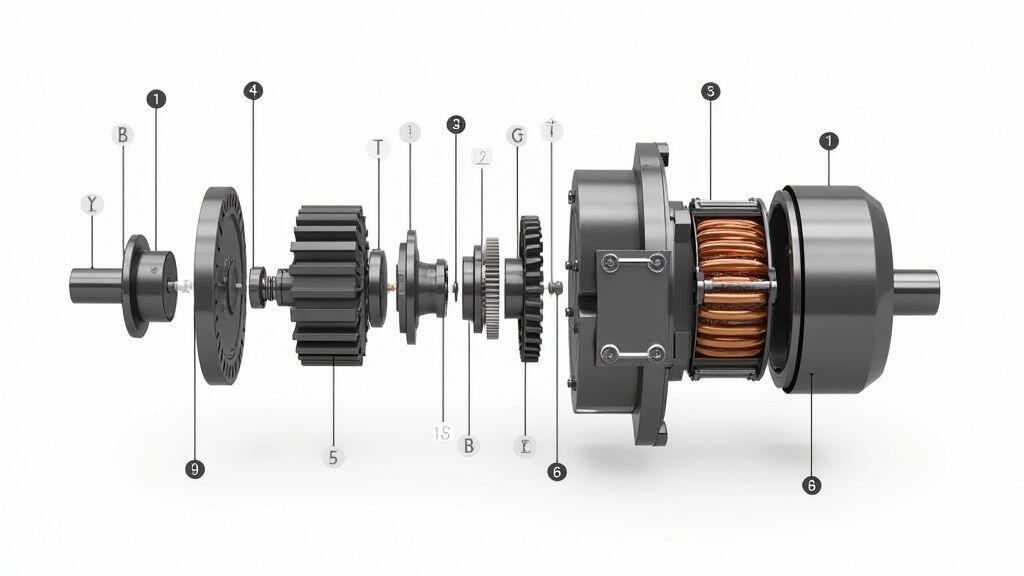

In today’s fast‑moving industrial landscape, production lines must keep pace with demand while keeping operating costs low. One of the unsung heroes behind this balance is the gear motor—a compact, robust device that drives conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other essential machinery. Recent advances in gear motor design have opened new possibilities for higher speeds and better energy efficiency, making them a key component in modern manufacturing floors.
A gear motor is essentially an electric motor integrated with a gear train. The motor provides the driving force, while the gears adjust the speed and torque to match the needs of the application. This combination reduces the need for separate drives and gearboxes, saving space and simplifying maintenance.

Why are they popular? Their compact size, high torque at low speeds, and straightforward installation make them ideal for many manufacturing tasks, from moving heavy payloads to fine‑tuned positioning in automation systems.
Speed is often a crucial factor in production rate. Modern gear motor models achieve higher speeds through several key strategies:
These improvements mean a manufacturing line can run faster without sacrificing reliability or product quality.
Operating cost is largely driven by energy consumption. Gear motor manufacturers now incorporate several features that reduce power usage:
Combined, these features can cut electricity bills by 10–20% while extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Upgrading to newer gear motor models delivers tangible advantages:
These benefits are especially critical for manufacturers dealing with fluctuating market demands and tight profit margins.
Integrating gear motors into existing production lines is now more straightforward thanks to modular designs and standardized interfaces. Manufacturers can retrofit older machinery or build new systems around smart, network‑connected gear motors.
Looking forward, the following trends are likely to shape gear motor technology:
These advancements promise even greater efficiencies and smarter manufacturing ecosystems in the coming years.
Gear motor models are rapidly evolving from basic power supplies into sophisticated, energy‑smart actuators that drive the future of manufacturing. By combining high‑torque motors, precise gear trains, and intelligent control systems, modern gear motors increase line speed and drastically cut energy consumption. For manufacturers, this translates to faster cycles, fewer breakdowns, and lower operating costs, thus reinforcing the competitiveness of production lines in an increasingly demanding market.
With the industry’s shift toward digitalization, sustainability, and agile production, gear motors will play an even more pivotal role. As they continue to become smarter and more efficient, adopting these models offers a clear path for factories seeking to stay ahead in the fast-paced manufacturing arena.
Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked